Human beings are characterized as multiplex. The human body is made up of millions of cells. The cells combine to form specific tissues. The tissues further join together to form organs.
Bone is made up of bony tissue. Bone consists of a matrix which is filled with a salt known as hydroxyapatite and collagen fibers. The bone’s internal structure resembles that of a honeycomb, which makes it rigid but light in weight.
There are approximately 206 bones in a human body, but it is believed that many accessory bones are present. The most significant bone in our body is the thighbone in layman term, medically it is known as the femur.
The smallest bone is present in the middle ear, the stapes.
Functions of the Human Bone
- Bone consists of the bone marrow, which is required for producing blood.
- The bone helps us structurally
- Protect significant organs of our body
- And most important it helps in locomotion
Two Major Types of Bone
- Cancellous bone is light and less dense
- Compact bone is hard, reliable, and durable.
The human skeleton has two major categories. The axial skeleton consists of the skull and spinal vertebrae. The appendicular frame consists of upper and lower limbs
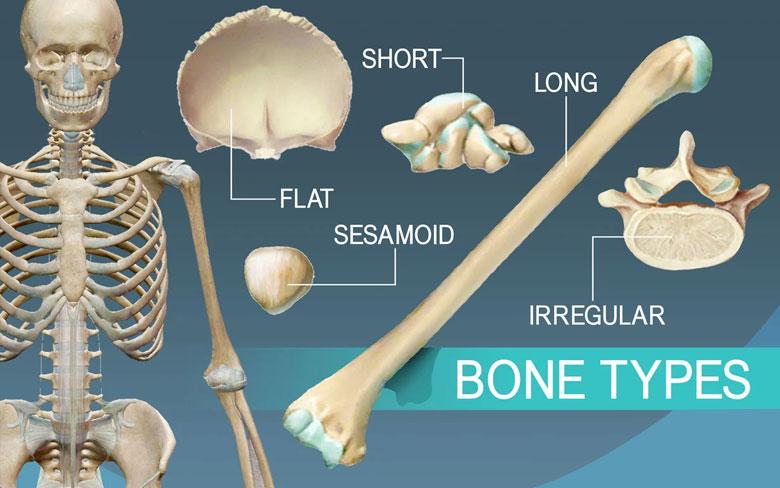
Five Types of Bones in the Human Skeleton
Long Bones
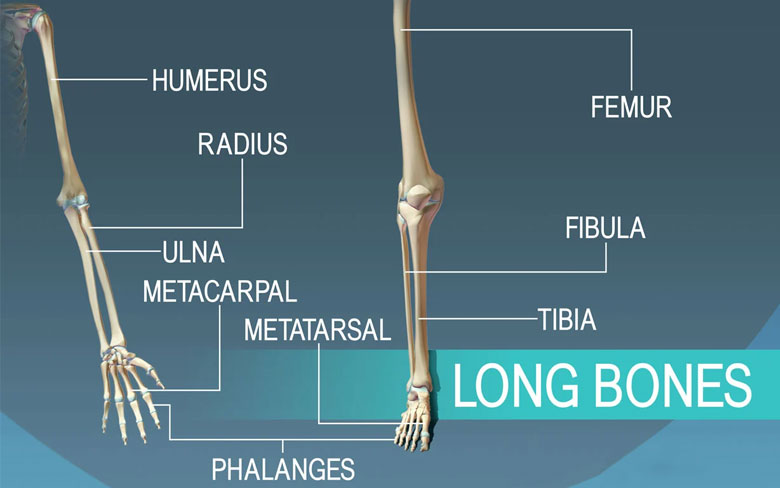
Long bones, as per the name, are long lengthwise but have a short width or base. These long bones are the example of compact bone. Hard and dense. And this characteristic helps them to facilitate body structurally and also to maintain the weight of the body. Our collection is mostly consisting of long bones, except ankles and wrist.
Long bones consist of a long shaft, which is called as diaphysis. The bony ends of the bone are round in shape and termed as epiphysis. The shaft or the diaphysis consists of the medullary cavity.
The femur, tibia, and metatarsals are all examples of the long bone. The clavicle, which is the beauty bone, has a curved shaft; thus, it is the modified long bone.
Short Bones
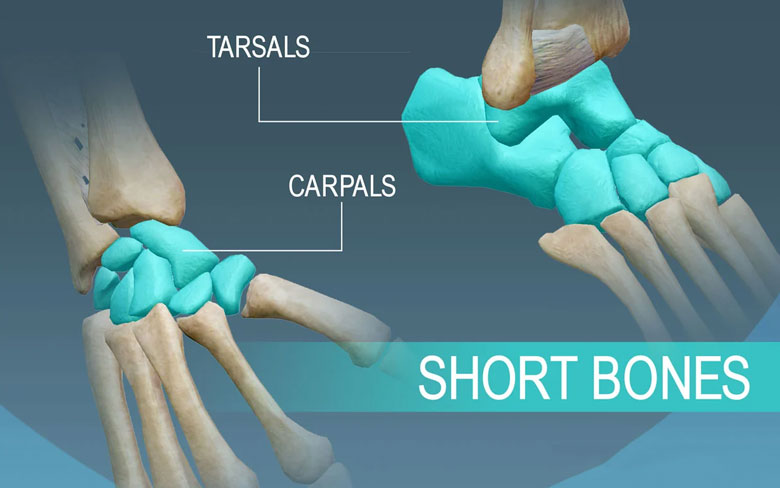
Short bones are also termed as cube-shaped bones. They have the same length and width. Their internal structure is spongy, and over the porous surface lies a single layer of compact bone. This helps them provide stability and little movement. Examples are the bones of our wrist and ankles.
Flat Bones
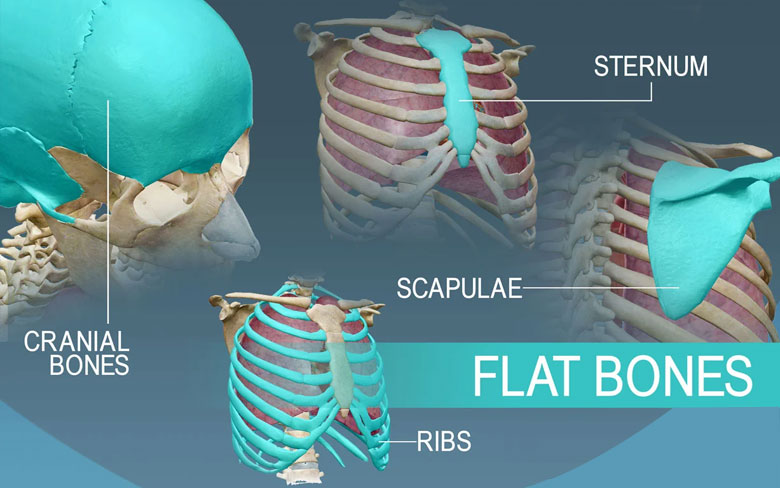
Flat bones consist of a broader surface and are usually thin but curved. These bones consist of a single layer of spongy bone, and the spongy bone is covered or sandwiched between the two layers of hard, compact bones. Their broad full surface provides muscle attachment and protects vital organs like heart and brain.
Examples are bones of the sternum and the skull, which involves the occipital bone, frontal bone, parietal bones, and temporal bones.
Irregular Bones
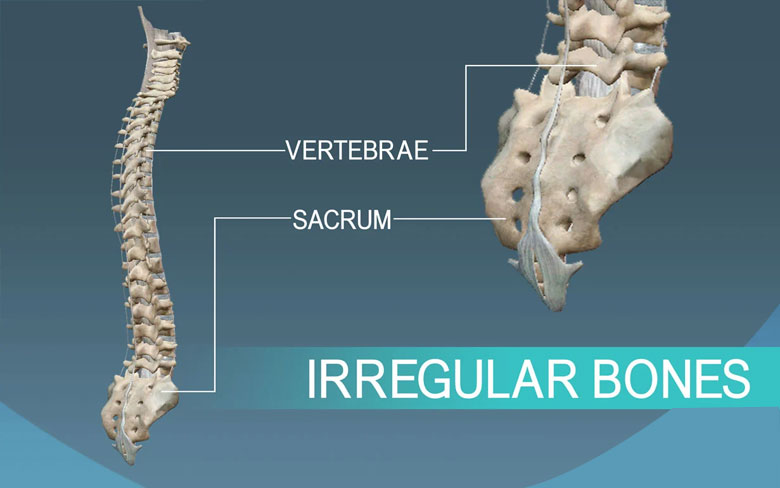
Irregular bone, as the name suggests they vary in size and their structure. They could be flat, long or short. But this characteristic helps them to protect our vital organs. The primary examples are the bones of the spinal cord, which protects the spinal cord and the hipbone.
Sesamoid Bones
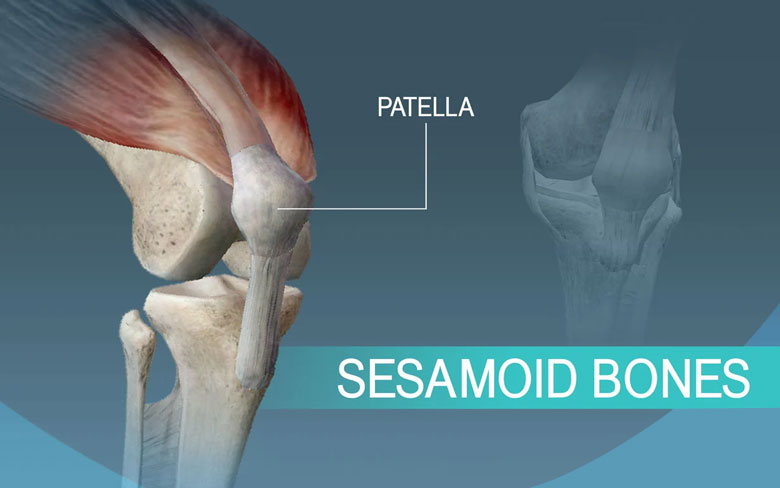
Sesamoid bones resemble the sesamoid seeds. Round and curved. There are incorporated with the tendons. These are present within the muscles of our hands and feet. The patella or the kneecap is the primary example of a sesamoid bone.
Three main methods do bone formation
- The intra-cartilaginous method that involves cartilage for bone formation
- The intramembranous way that requires osseous tissue or membrane
- And last is the intra-cartilage membranous method.
Conclusion
Adequate intake of calcium and minerals will keep our bones healthy and strong. And our bones, in return, will help us structurally and will protect the vital organs of our body.
